Ho-Hsi Cheng†, Yuan-Bin Cheng‡, Tsong-Long Hwang§⊥∥, Yao-Haur Kuo#, Chung-Hsiung Chen†, and Ya-Ching Shen*†
† School of Pharmacy, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei 100, Taiwan
‡ Graduate Institute of Natural Products, College of Pharmacy, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung 807, Taiwan§
Graduate Institute of Natural Products, School of Traditional Medicine, College of Medicine, and Chinese Herbal Medicine Research Team, Healthy Aging Research Center, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan 33302 Taiwan
⊥ Department of Cosmetic Science and Research Center for Industry of Human Ecology, Chang Gung University of Science and Technology, Taoyuan 33302, Taiwan
∥ Immunology Consortium, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan 33302, Taiwan
# Division of Herbal Drugs and Natural Products, National Research Institute of Chinese Medicine, Taipei 112, Taiwan
J. Nat. Prod., 2015, 78 (8), pp 1823–1828
Abstract

Four new compounds, randainins A–D (1–4), were isolated from the leaves and twigs of Callicarpa randaiensis, which is an endemic species in Taiwan. Compounds 1 and 2 are diterpenoids with an unusual trans-7/5 ring system, whereas compounds 3 and 4 are diterpenoids possessing a trans-5/7 ring scaffold. The structures of the new compounds were established based on NMR and MS data analyses. Anti-inflammatory activities and cytotoxicity were tested and evaluated for these compounds. Compound 4 exhibited moderate inhibition of superoxide-anion generation with an IC50 value of 21.5 ± 2.5 μM. (新骨架化合物)
Abstract

Investigation of the leaves and twigs of Callicarpa longissima resulted in the isolation of four new compounds (1–4), callilongisins A–D, and five known compounds, ursolic acid, 3-oxoanticopalic acid, (E)-6β-hydroxylabda-8(17),13-dien-15-oic acid, 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,4′-tetramethoxyflavone, and artemetin. Compounds 1–3 are 3,4-seco-abietane-type diterpenoids, and compound 4 is an analogue of a labdenoic-type diterpene. The structure of compound 1 was confirmed by X-ray crystallographic analysis. Cytotoxicity against a human prostate cancer cell line (PC3) and anti-inflammatory activities of the isolated compounds were evaluated.
Abstract

Fractionation of an acetone extract from the fruits of Schisandra arisanensis afforded five new nortriterpene lactones, compounds 1−5, together with four known compounds, schindilactones D and E (6 and 7) and preschisanartanins A and B (8 and 9). Compound 1, a wuweiziartane-type nortriterpenoid, possesses a new type of fused ring system with a γ-lactone ring between C-15 and C-17. Compounds 2, 6, and 7 may be categorized as schisanartane-type nortriterpenoids and compounds 3−5, 8, and 9 as preschisanartane-type nortriterpenoids. The structures of the new compounds were elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic data interpretation. The structure and relative configuration of 3 were supported by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The antiviral activity against HSV-1 and inhibitory effects on superoxide anion generation and elastase release by human neutrophils in response to FMLP/CB of compounds 1−9 were evaluated.
J. Nat. Prod., 2008, 71 (9), pp 1551–1556
Abstract

Chemical investigation of the gorgonian octocoral Junceella fragilis, collected in Taiwan, resulted in the isolation of seven new briarane-type diterpenes, frajunolides E−K (1−7), in addition to 14 known briaranes, praelolide, junceellin, junceellolides A−E, and K, 11a,20a-epoxy-4-deacetoxyjunceelolide D, umbraculolide A, junceellonoid A, and juncins Y, Z, and ZI, as well as ergosterol peroxide. The structures of 1−7 were determined by analysis of HRESIMS and 2D NMR spectroscopic data. Cytotoxicity and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities of compounds 1−7 were also evaluated.
Abstract

Ten new derivatives (2−11) of ambrein (1), isolated from ambergris, were prepared by chemical transformation. Oxidation and/or cyclization were effected by reactions with selenium oxide or p-toluenesulfonyl chloride or with the use of shortwave UV light. The structures of 2−12 were elucidated by spectroscopic analysis, with the structure and relative configuration of 9 confirmed by single-crystal X-ray crystallography. The cytotoxic activities of 1−12 were investigated against human liver carcinoma (Hepa59T/VGH), colon adenocarcinoma (WiDr), lung carcinoma (A-549), and human breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) cell lines. The anti-inflammatory activities of 1−11, in terms of the inhibition of human neutrophil function, were also evaluated. (香料)
Abstract

Six new xenicane-type diterpenoids, designated as asterolaurins A−F (1−6), have been isolated from the organic extract of the soft coral Asterospicularia laurae, collected in southern Taiwan. Compounds 1−4 possess a xenicin skeleton with a 2-oxabicyclo[7.4.0]tridecane ring system, while 5 and 6 are xeniolide A-type compounds. The structures of the new secondary metabolites, including their configurations, were established on the basis of an extensive spectroscopic analysis, including 1D and 2D NMR (1H−1H COSY, HMQC, HMBC, and NOESY), and by comparison of their NMR data with those of the related compounds. The structure of asterolaurin A (1) was confirmed by X-ray diffraction analysis, and its absolute configuration was determined using the modified Mosher’s method. Asterolaurin A (1) exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells with an IC50 of 8.9 μM, while asterolaurin D (4) showed potent inhibition of elastase release and superoxide anion generation in vitro.
Abstract
Ten new briarane diterpenoids, briaviolides A–J (1–10), together with six known briaranes, solenolides A and D, excavatolide A, briaexcavatolide I, 4β-acetoxy-9-deacetystylatulide lactone and 9-deacetylstylatulide lactone, were isolated from the Taiwanese soft coral, Briareum violacea. Their structures were determined on the basis of spectroscopic data (1H- and 13C-NMR, 1H–1H COSY, HSQC, HMBC and NOESY), HR-MS and chemical methods. The absolute configuration of briaviolide A (1) was determined by X-ray crystallographic analysis. Compounds 5, 9 and derivative 11 showed moderate inhibitory activities on superoxide-anion generation and elastase release by human neutrophils in response to N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine/ Cytochalasin B (fMLP/CB).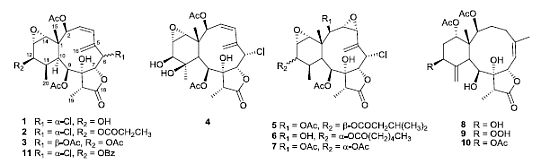
8. Seven New Sesquiterpenoids from the Fruits of Schisandra sphenanthera (華中五味子)
Yao‐Ching Tsai, Yuan‐Bin Cheng, I‐Wen Lo, Ho‐Hsi Cheng, Ching‐Jie Lin, Tsong‐Long Hwang, Yuh‐Chi Kuo, Shorong‐Shii Liou , Yi‐Zsau Huang, Yao‐Haur Kuo,Ya‐Ching Shen*
Chemistry & BiodiversityVolume 11, Issue 7
987-1120
July 2014
Abstract
Fractionation of the EtOH extract from the fruits of Schisandra sphenanthera resulted in the isolation of seven new sesquiterpenoids, 1–7, in addition to the known metabolites 8–23. Among them, schiscupatetralin A (1) possesses an unprecedented structure with a CC bond between cuparenol and tetralin. The isolated new compounds were evaluated for their anti‐HSV‐1 and anti‐inflammatory activities. The results revealed that compound 4 exhibited anti‐HSV‐1 activity, while compound 6showed a significant anti‐inflammatory activity.

